Prepper Sage participates in various affiliate marketing programs, including Amazon, which means we may get paid commissions on purchases made through our links to retailer sites.

In a world where staying connected and powered up is essential, especially during outdoor adventures or emergencies, the choice between a portable power station and a portable generator can make a significant difference. Both devices provide backup power, but they serve different purposes and come with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right solution for your needs, whether you’re camping, working on a remote job site, or preparing for unexpected power outages. This blog post will explore the key differences between portable power stations and portable generators, examining their features, benefits, and drawbacks to help you make an informed decision.
Portable Power Stations

Portable power stations are becoming increasingly popular as a versatile and eco-friendly alternative to traditional generators. These devices are essentially large batteries that store electrical energy, which can be used to power various electronic devices and small appliances. They are designed for ease of use, portability, and efficiency, making them ideal for a range of applications.
How Portable Power Stations Work
Portable power stations operate by storing energy in internal
batteries, usually lithium-ion, which can be charged through multiple
sources such as solar panels, wall outlets, or even car chargers.
Once charged, these stations can power devices via USB ports, AC
outlets, and DC carports. They are typically used for charging
laptops, phones, small kitchen appliances, and even medical devices
like CPAP machines.
Applications of Portable Power Stations
These power stations are particularly popular among outdoor enthusiasts, campers, and RV owners. They provide a quiet, clean, and reliable source of power in remote locations where traditional electricity is unavailable. Additionally, they are useful for home backup during power outages, ensuring that essential devices remain operational. Portable power stations are also favored in situations where noise levels need to be minimal, such as in campsites or residential areas.
Portable Power Stations Environmental Impact
One of the biggest advantages of portable power stations is their minimal environmental impact. Unlike generators that burn fuel, these stations produce no emissions, making them a much cleaner option. This eco-friendly characteristic is particularly important for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint or comply with regulations in areas where fuel-burning devices are restricted.
Pros of Portable Power Stations
1. Quiet Operation: Portable power stations operate silently, making them ideal for use in noise-sensitive environments.
2. Eco-Friendly: With no fuel consumption or emissions, they are a greener choice.
3. Ease of Use: These devices are user-friendly, with simple plug-and-play functionality.
Cons of Portable Power Stations
1. Limited Power Capacity: They may not be able to power larger appliances or tools for extended periods.
2. Longer Recharge Times: Recharging can take several hours, especially if using solar panels.
3. Higher Initial Cost: Portable power stations tend to be more expensive upfront compared to generators.
Portable Generators
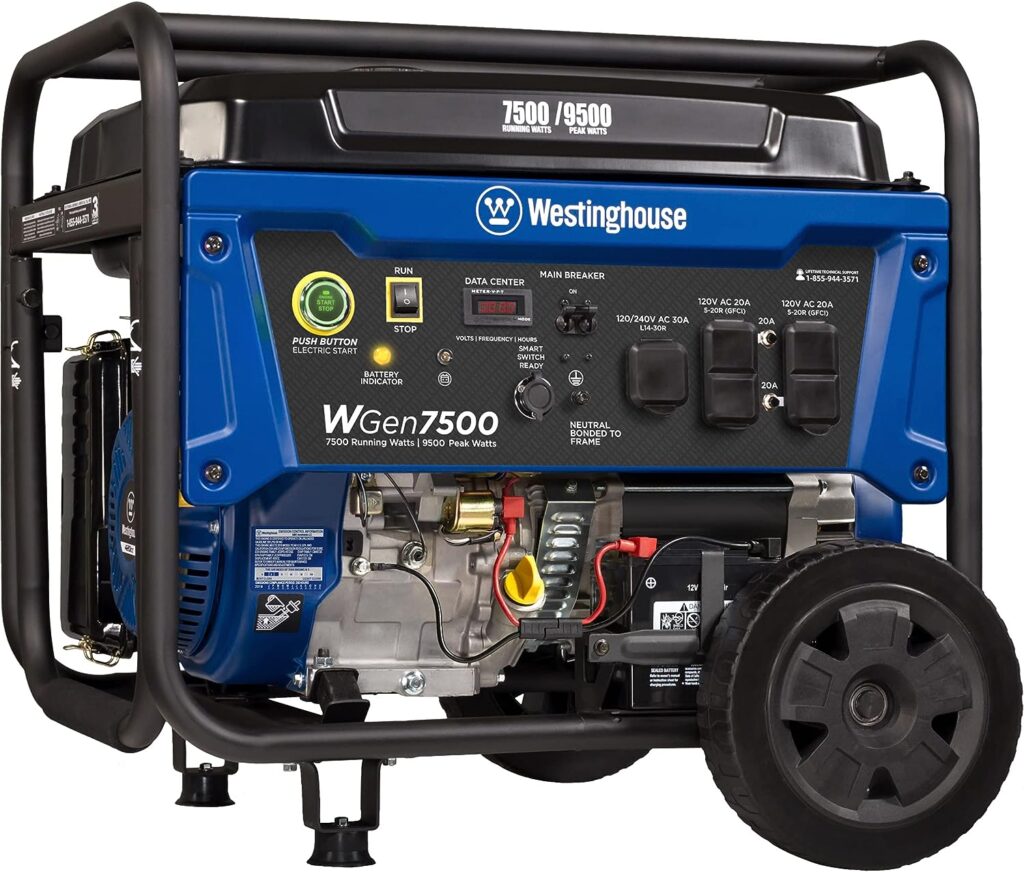

Portable generators have been the go-to solution for backup power for many years. They are powerful, reliable, and capable of running larger appliances and tools, making them suitable for a variety of situations, from home emergencies to outdoor work sites.
How Portable Generators Work
Portable generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by burning fuel, usually gasoline, propane, or diesel. This process powers a built-in alternator that produces electricity, which can then be used to run household appliances, power tools, or even an entire home in some cases. Generators typically have multiple outlets, allowing you to connect and run several devices simultaneously.
Applications of Portable Generators
These generators are highly versatile and are commonly used in emergency situations to provide power during outages. They are also widely used on construction sites to run heavy machinery and tools where access to electricity is limited. For outdoor enthusiasts, portable generators can power larger devices that a power station might not handle, such as electric grills, RV air conditioners, and lighting systems.
Portable Generators Fuel and Maintenance Considerations
One of the key factors to consider when using a portable generator is fuel. They require regular refueling, and the type of fuel can affect both the generator’s efficiency and environmental impact. Additionally, portable generators need ongoing maintenance, such as oil changes and air filter replacements, to ensure they run smoothly. Proper storage of fuel and the generator itself is also crucial to avoid safety hazards.
Pros of Portable Generators
1. High Power Output: Generators can handle larger loads and run multiple devices simultaneously.
2. Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from home backup to powering tools on a job site.
3. Availability: They are widely available and come in various sizes and power capacities to suit different needs.
Cons of Portable Generators
1. Noise Levels: Generators can be quite loud, which might not be suitable for all environments.
2. Environmental Impact: They emit fumes and require fossil fuels, contributing to pollution.
3. Maintenance Requirements: Generators require regular upkeep, including fuel management and mechanical maintenance.
Conclusion
Choosing between a portable power station and a portable generator depends largely on your specific needs, intended use, and environmental considerations. Portable power stations are an excellent choice for those who prioritize quiet operation, eco-friendliness, and ease of use, especially in low-power situations. On the other hand, portable generators are more suited for high-power needs, offering versatility and reliability in a variety of settings but requiring more maintenance and having a greater environmental impact.
Ultimately, understanding the differences between these two power solutions will help you make the best choice for your situation, whether you’re preparing for an outdoor adventure, need backup power at home, or require a reliable power source for your worksite. By weighing the pros and cons of each, you can select the option that best meets your needs and ensures you stay powered up, no matter where you are.
Amazon and the Amazon logo are trademarks of Amazon.com, Inc, or its affiliates.